3.3V ↔ 5V Conversion
The operating voltage of Raspberry Pi’s GPIO input/output pins is 3.3V. Therefore, to connect 5V-only sensors and modules or to communicate with devices that operate at 5V such as Arduino, 5V ↔ 3.3V conversion is absolutely necessary.
There are mainly two methods for voltage conversion as shown below.
Voltage Divider
A voltage divider refers to a circuit configured as shown below that uses resistors to reduce voltage.
According to Ohm’s law, the output voltage of a voltage divider can be calculated using the following formula:
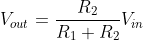
For example, to connect a sensor that outputs 5V to a Raspberry Pi, when the voltage needs to be reduced to 3.3V, using R₁: 1kΩ and R₂: 2kΩ will output Vout = (2/3)*5V = 3.3V.
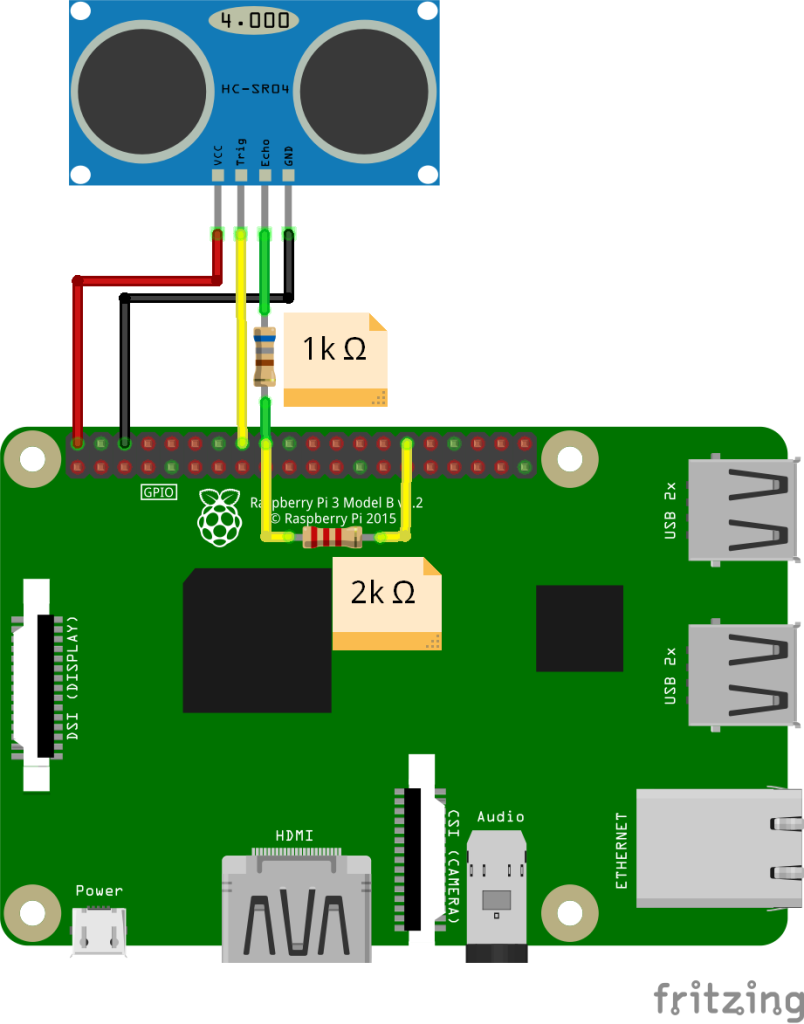
Below is an example of connecting an HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor to a Raspberry Pi through a voltage divider. Since the Echo pin output of HC-SR04 is 5V, the voltage must be reduced to 3.3V before connection.
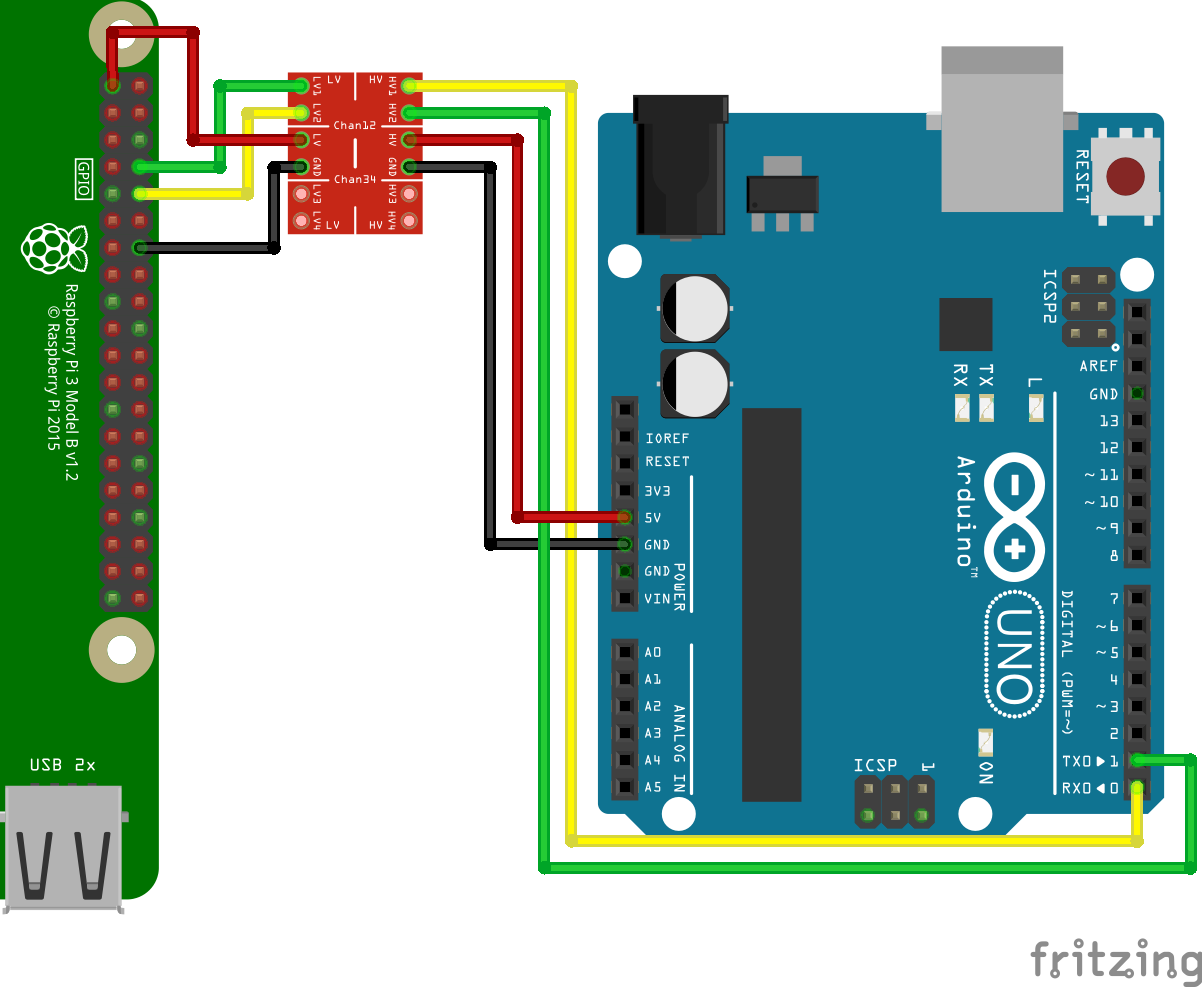
Logic Level Converter
A module that can increase or decrease voltage in one direction (uni-directional) or convert voltage in both directions (bi-directional).
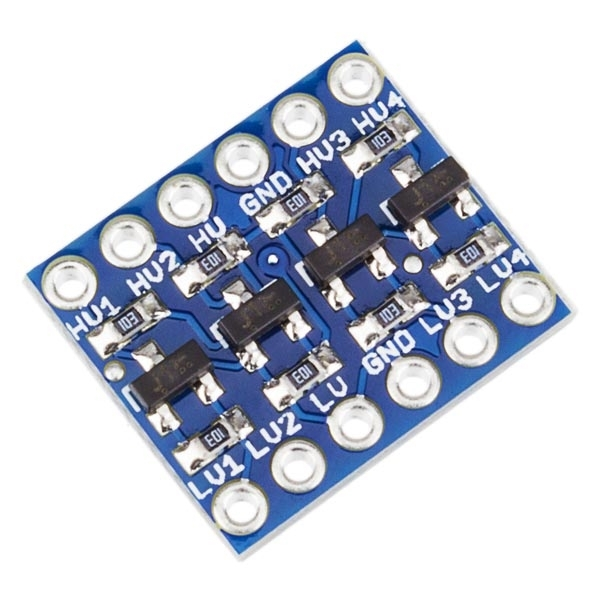
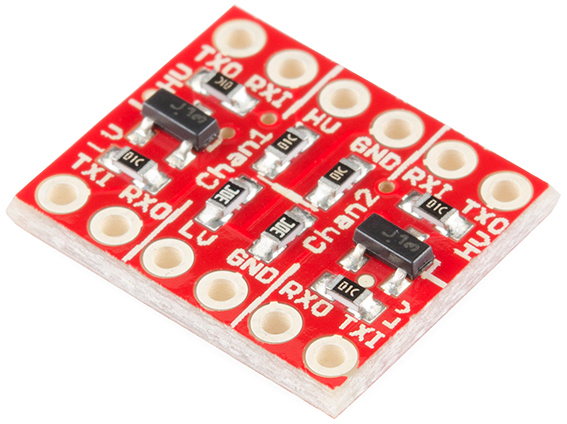
Usually, one module supports multiple channels, allowing multiple devices to be connected simultaneously, and can be used in the following cases:
- Connecting 3.3V output sensors or modules to 5V devices
- Connecting 5V output sensors or modules to 3.3V devices
- Communication between 3.3V devices and 5V devices
• 5V devices: Arduino Uno, Arduino Nano, Arduino Mega, Arduino Leonardo, etc.
Below is an example of UART communication connection between Arduino Uno and Raspberry Pi using a bidirectional logic level converter. (Note that the higher voltage should be connected to HV and the lower voltage to LV)