DC Motor, Servo Motor, Stepper Motor
A motor is a device that converts electrical energy into rotational energy, also called an electric motor. There are various types of motors depending on the power source type and structure, but the motors mainly used in Arduino and Raspberry Pi are DC motors, servo motors, and stepper motors. Since each motor has different purposes, you must select the appropriate motor for your intended purpose.
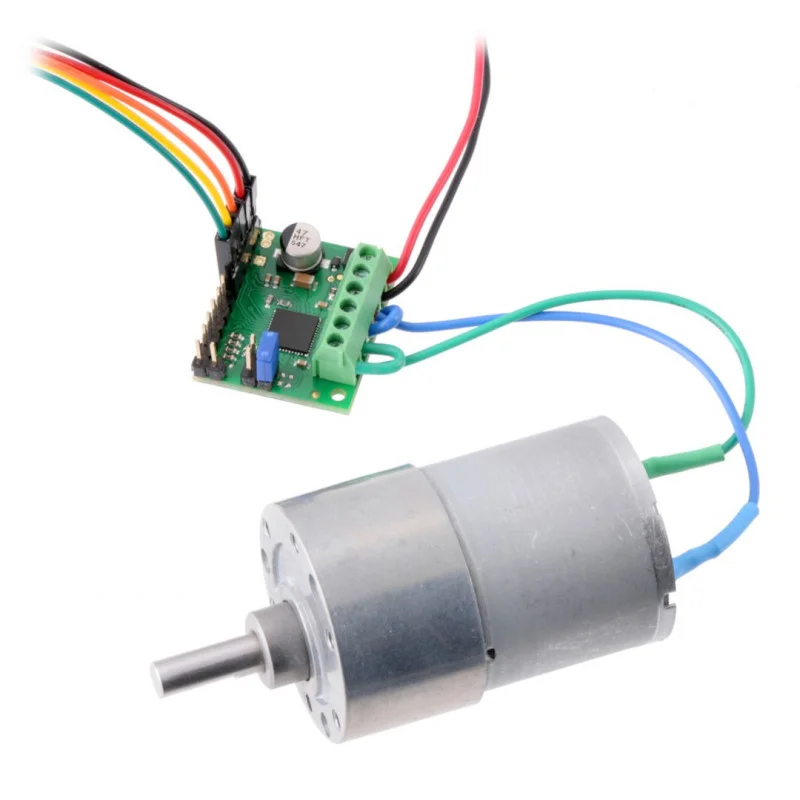
DC Motor
A motor used for continuous rotation purposes, such as in portable fans and radio-controlled cars (RC cars), and is the most widely used motor in various fields. It has high starting torque characteristics and output torque proportional to input current.
When power is connected to the + and – terminals, it rotates in the forward direction, and when the polarity is reversed, it rotates in the reverse direction. Using a motor driver enables forward/reverse rotation control and speed control using PWM signals.

Servo Motor
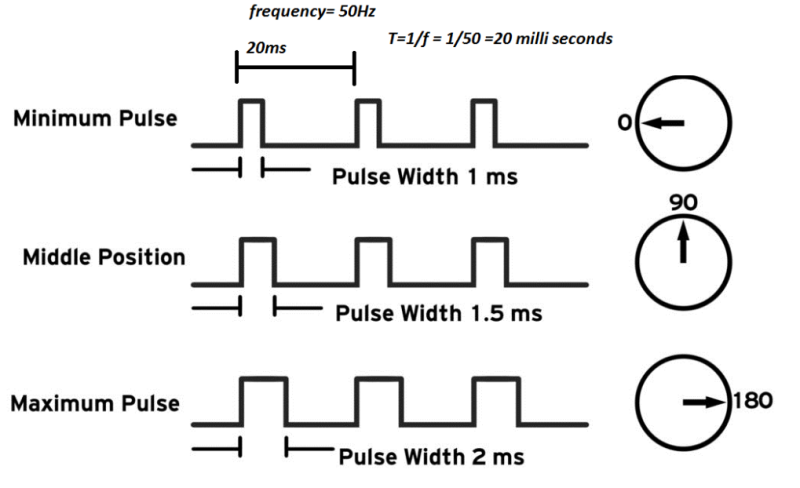
Servo motors used in Arduino and Raspberry Pi are commonly called RC servo motors and are used for purposes such as steering adjustment in RC cars. They have the characteristic of rotating and maintaining angles from 0 to 180 degrees according to the pulse width of PWM signals. They are not suitable for continuous rotation or speed control purposes and are motors used when specific angle control is required.

• Current must be supplied from an appropriate external power source considering the servo motor’s voltage and current consumption.
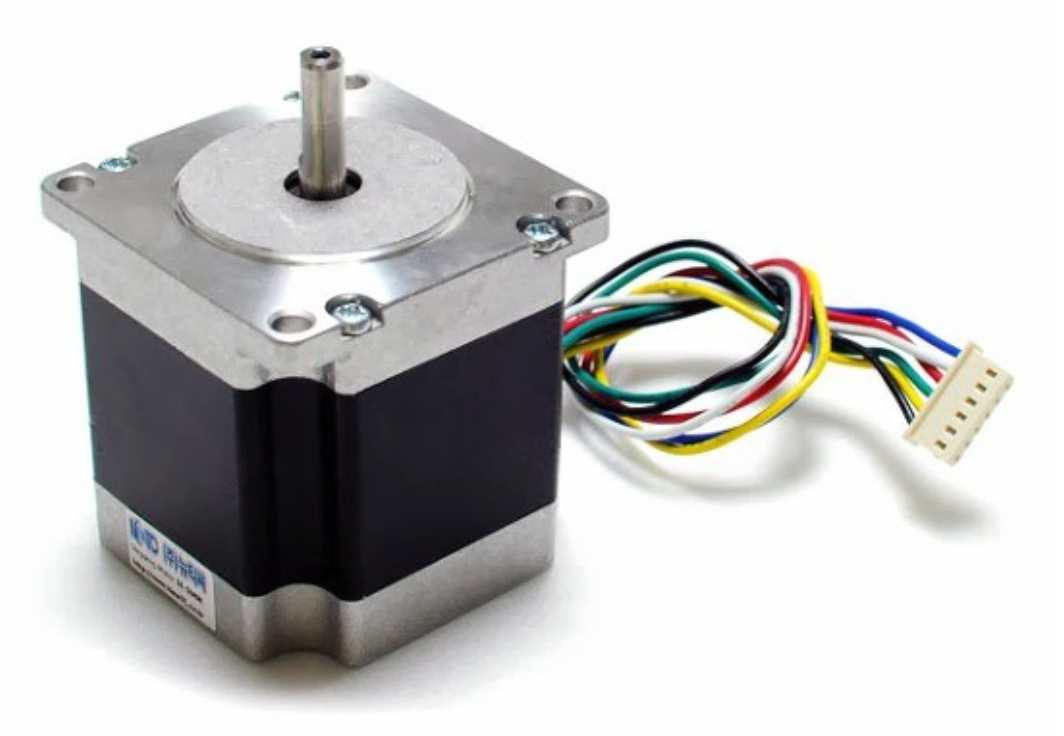
Stepper Motor
A motor that rotates one step for each input pulse signal. It has high resolution and can be used for high-precision position control or speed control. It is mainly used in places requiring precise control, such as 3D printers and industrial production equipment. It is driven using stepper motor drivers such as the A4988, and the controller must send continuous pulse signals to the driver at precise timing for the number of steps to be rotated.