Installing Linux on macOS (Virtual Machine)
Using virtualization software, you can install Linux on macOS and use it as a Grablo controller.
Linux Download
Grablo controller software runs on Debian-based Linux distributions (Debian, Ubuntu, Mint, Zorin OS, etc.), and we recommend Debian Linux as the most stable and lightweight distribution. Visit here to download the distribution image that matches your PC’s architecture.
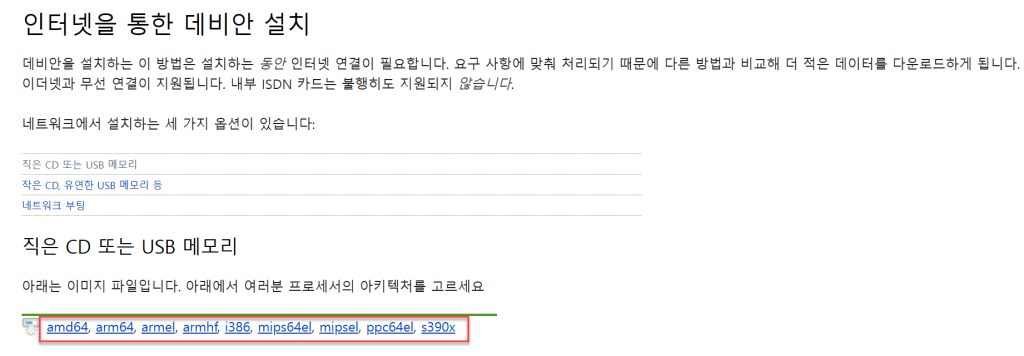
– amd64: Intel Mac
– arm64: Apple Silicon Mac (M1, M2, M3…)
Installing Virtualization Software
Virtualization software available for macOS includes VMware, UTM, etc., but we recommend VMware as it is the most widely used and feature-rich. Visit here to download and install the latest version of VMware Fusion Pro. It’s free for personal users and requires Broadcom membership registration.
Run VMware, click [+], then click [New].

Drag and drop the downloaded Linux distribution image to the upper area.
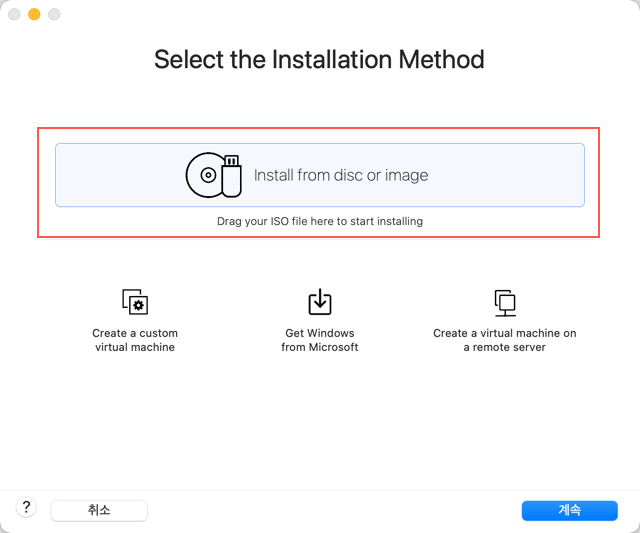
Information about the Linux to be installed will be displayed. Click [계속].
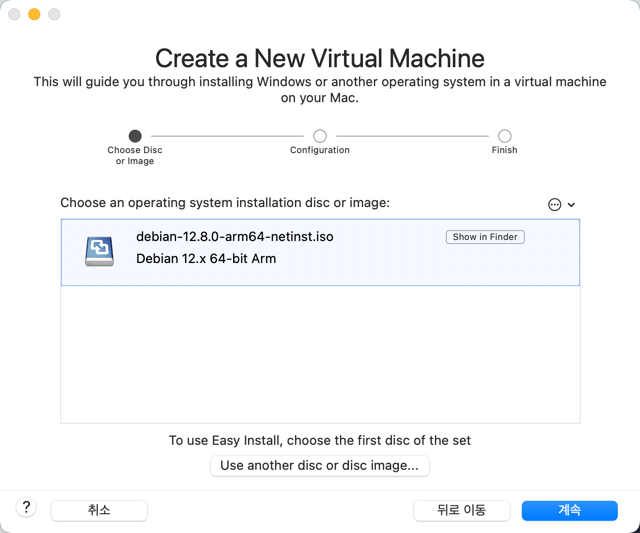
The specifications of the virtual machine to be created will be displayed. If you want to change the specifications, click [Customize Setting] to modify them. Click [Finish].
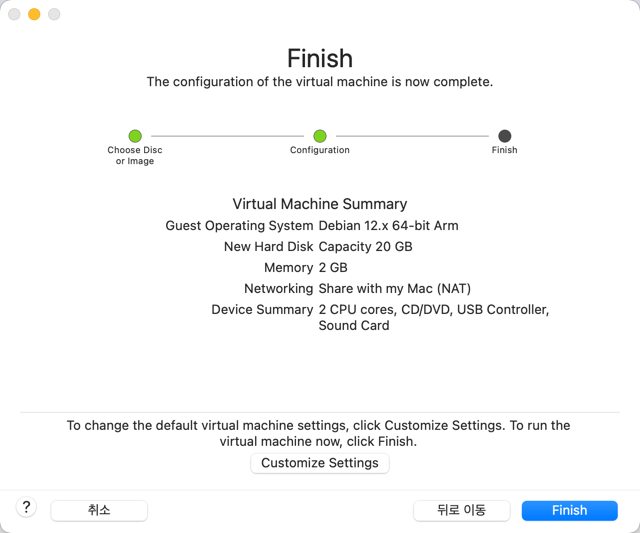
Set the virtual machine name and storage location, then click [저장]. The virtual machine will automatically boot and enter the Linux installation screen.
Linux Installation
The Linux installation process is identical to Installing Linux on Windows (Virtual Machine), so please refer to that content.
