DC Motor Control
Overview
A library for controlling DC motors using PWM signals. DC motors are driven through motor drivers, and various types of drivers exist.

The types and descriptions of DC motor drivers are as follows:
| Type | Description | Models |
|---|---|---|
| Type 1 |
• ENA/B: Speed control |
L298N, L293D, TB6612FNG, etc. |
| Type 2 | • IN1: Forward speed control • IN2: Reverse speed control |
L9110, DRV8833, etc. |
| Type 3 | • DIR: Forward/reverse direction control • PWM: Speed control |
MAX14870, etc. |
Supported GPIO
- Raspberry Pi 0~4
- Raspberry Pi 5
- BeagleBone Black/Green
- Jetson Nano
Commands
[INIT]
Enters initial configuration settings.
| Item | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Driver Type | WRITE | Select the motor driver type. (Type 1, Type 2, Type 3) |
When Type 1 (ENA, IN1, IN2) is selected:
| Item | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ENA/B Pin | WRITE | Enter the GPIO pin number to connect to the ENA/B pin or select a PWM pin. |
| IN1 Pin | WRITE | Enter the GPIO pin number to connect to the IN1 pin. Controls forward/reverse direction. |
| IN2 Pin | WRITE | Enter the GPIO pin number to connect to the IN2 pin. Controls forward/reverse direction. |
When Type 2 (IN1, IN2) is selected:
| Item | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IN1 Pin | WRITE | Enter the GPIO pin number to connect to the IN1 pin or select a PWM pin. |
| IN2 Pin | WRITE | Enter the GPIO pin number to connect to the IN2 pin or select a PWM pin. |
When Type 3 (DIR, PWM) is selected:
| Item | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DIR Pin | WRITE | Enter the GPIO pin number to connect to the DIR pin. Controls forward/reverse direction. |
| PWM Pin | WRITE | Enter the GPIO pin number to connect to the PWM pin or select a PWM pin. |
[RUN]
Runs the motor in the specified direction and speed.
| Item | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Rotation Direction | WRITE | Enter the rotation direction. True for forward, false for reverse. |
| Rotation Speed | WRITE | Enter the rotation speed. (0~100%) |
| Acceleration (%/s) | WRITE | Enter the acceleration rate. (Enter 0 if not used) |
| Deceleration (%/s) | WRITE | Enter the deceleration rate. (Enter 0 if not used) |
[COAST_STOP]
Allows the motor to slowly stop due to inertia. (free running stop)
[HARD_STOP]
Stops the motor immediately.
Example
Objective
Control rotation direction using dashboard switch widgets and control speed using slider widgets.
Parts
| Part | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Raspberry Pi 4 * | 1 |
| DC Motor | 1 |
| L298N Driver | 1 |
| 12V DC Power Supply | 1 |
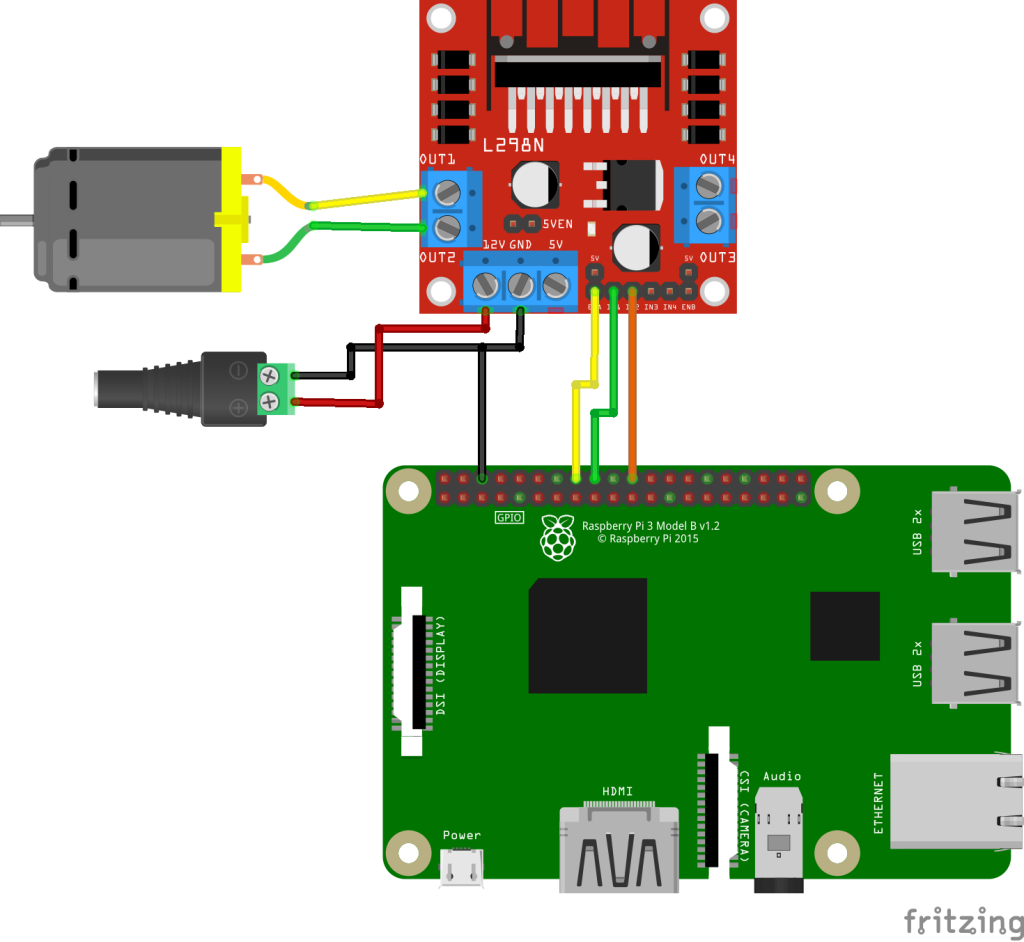
Wiring
Connect each component to the corresponding connection as listed in each row below.
| 5~35V DC Power ¹ | DC Motor | L298N | GPIO |
|---|---|---|---|
| | ENA | 23 ² | |
| | IN1 | 24 | |
| | IN2 | 25 | |
| + | 12V | | |
| – | GND | GND | |
| 5V | 5V (Optional) ³ | ||
| Pin 1 | OUT1 | ||
| Pin 2 | OUT2 |
2. Raspberry Pi 0~4 can use any GPIO pins, while other hardware can only use PWM output pins.
3. If the external DC power supply is less than 7V, the onboard 5V regulator will not work properly, so you must supply 5V separately to the board’s 5V terminal. In this case, you must remove the 5V-EN jumper to disable the internal regulator, otherwise voltage conflicts may occur. Conversely, if the external DC power supply is 7V or higher, the 5V-EN jumper should be inserted to use the internal regulator, and in this case, you must never connect the Raspberry Pi’s 5V to the board’s 5V terminal. Otherwise, the board or Raspberry Pi may be damaged, so be careful.
Project Links
