QMC5883L 3-Axis Magnetometer
Overview
QMC5883L is a 3-axis magnetometer sensor that can be used for electronic compass or direction detection by measuring the Earth’s magnetic field. Uses I2C interface.
Specifications
- Operating Voltage: 2.0V ~ 3.6V
- Communication Interface: I2C (2-wire, up to 400kHz)
- Output Data: 16-bit digital (X, Y, Z axes)
- Measurement Range (Sensitivity Setting): ±2, ±8 Gauss (user configurable)
- Resolution:
- Approximately 0.061 μT/LSB (≈ 0.61 mG/LSB) at ±2 Gauss
- Approximately 0.24 μT/LSB (≈ 2.44 mG/LSB) at ±8 Gauss
- Sampling Rate (ODR): Up to 200Hz
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C ~ +85°C
- Current Consumption: Average approximately 75 μA (based on measurement mode, very low power)
- Accuracy (Azimuth Error): ±1–2° (varies depending on calibration status and environment)
Supported GPIO
- Raspberry Pi 0~4
- Raspberry Pi 5
- BeagleBone Black/Green
- Jetson Nano
- FT232H, FT2232H, FT4232H
- MCP2221
Commands
[READ_MAG]
Reads 3-axis magnetometer values. The unit is microtesla (uT).
| Item | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetometer X-axis (uT) | READ | X-axis magnetometer value. |
| Magnetometer Y-axis (uT) | READ | Y-axis magnetometer value. |
| Magnetometer Z-axis (uT) | READ | Z-axis magnetometer value. |
[GET_HEADING]
Calculates the heading angle.
| Item | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Heading Angle (º) | READ | Calculated heading angle. |
The QMC5883L sensor measures direction (heading angle) using the Earth’s magnetic field. However, the reference at this time is not True North but Magnetic North, which is where the Earth’s magnetic field points.
Since the Earth’s magnetic field direction varies slightly by region, there is an angular difference between magnetic north and true north. This angular difference is called Magnetic Declination.
Therefore, if you want to know the accurate direction based on true north, you need to correct it by adding or subtracting the magnetic declination to the magnetic north-based heading angle.
Magnetic declination changes continuously, and you can refer to here for the current magnetic declination at your location and time.
Since the Earth’s magnetic field direction varies slightly by region, there is an angular difference between magnetic north and true north. This angular difference is called Magnetic Declination.
Therefore, if you want to know the accurate direction based on true north, you need to correct it by adding or subtracting the magnetic declination to the magnetic north-based heading angle.
Magnetic declination changes continuously, and you can refer to here for the current magnetic declination at your location and time.
Example
Objective
Display 3-axis magnetometer values and heading angle measured by the sensor on dashboard widgets.
Parts
| Part | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Raspberry Pi 4 * | 1 |
| QMC5883L | 1 |
* Other hardware can also be used. Refer to Supported GPIO.
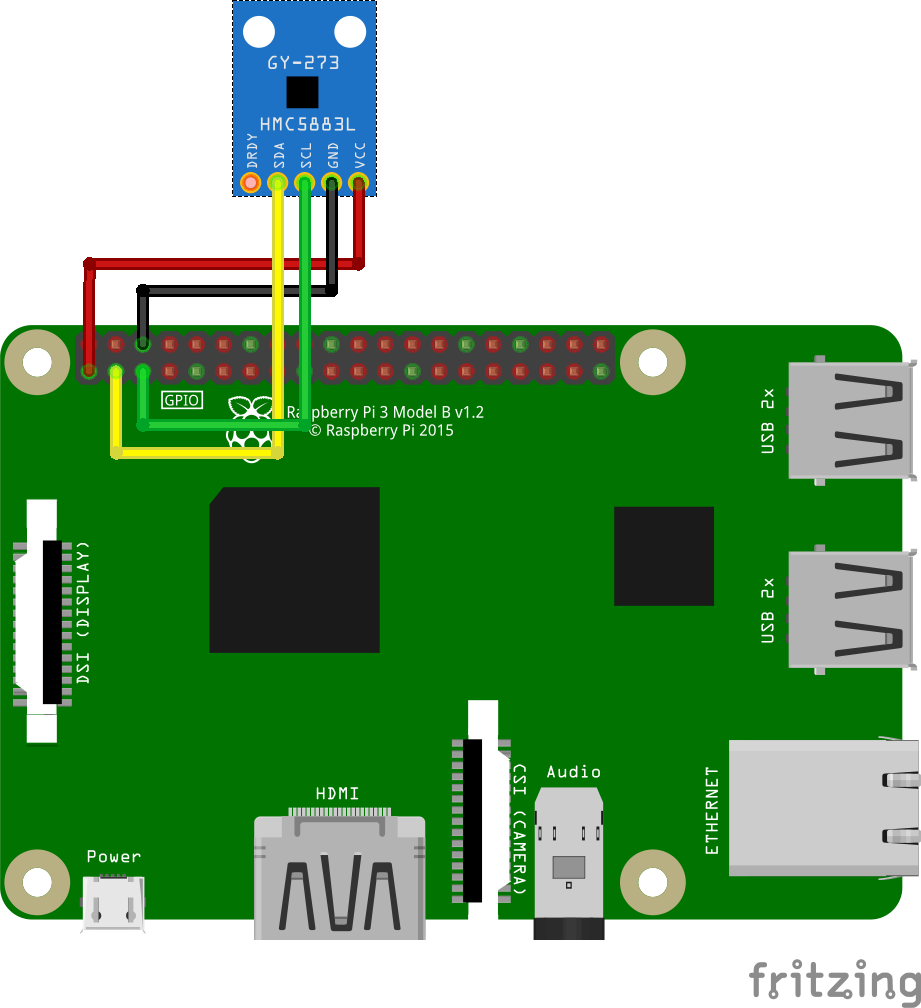
Wiring
Connect each component to the corresponding connection as listed in each row below.
| QMC5883L | GPIO |
|---|---|
| VCC | 3.3V |
| GND | GND |
| SCL | 3 (I2C1 SCL) |
| SDA | 2 (I2C1 SDA) |