Modbus Communication
An action that communicates using the Modbus protocol.
Modbus is an industrial protocol developed in 1979 for communication between automation devices. It is widely used across various industrial sectors to implement simple, reliable, and efficient communication.
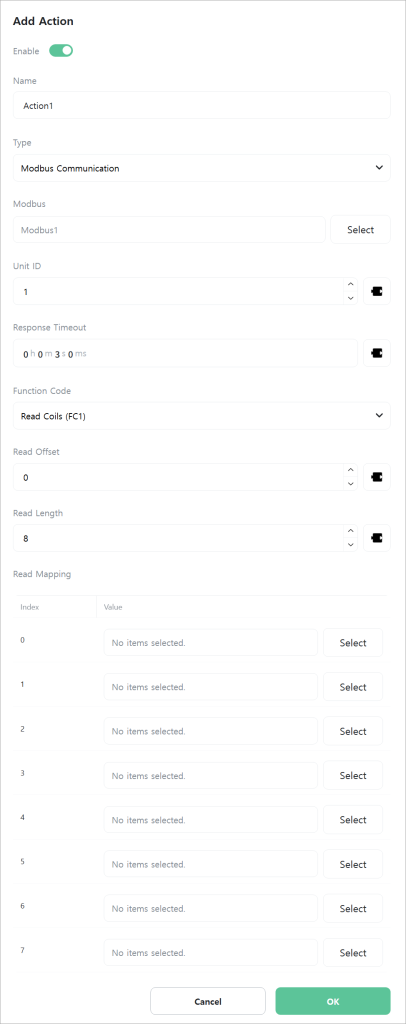
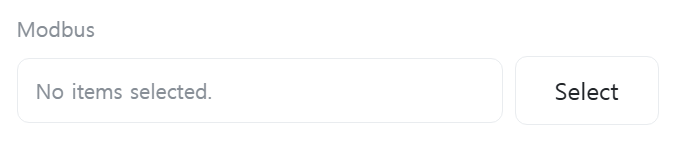
[Modbus]
Select the Modbus to use.
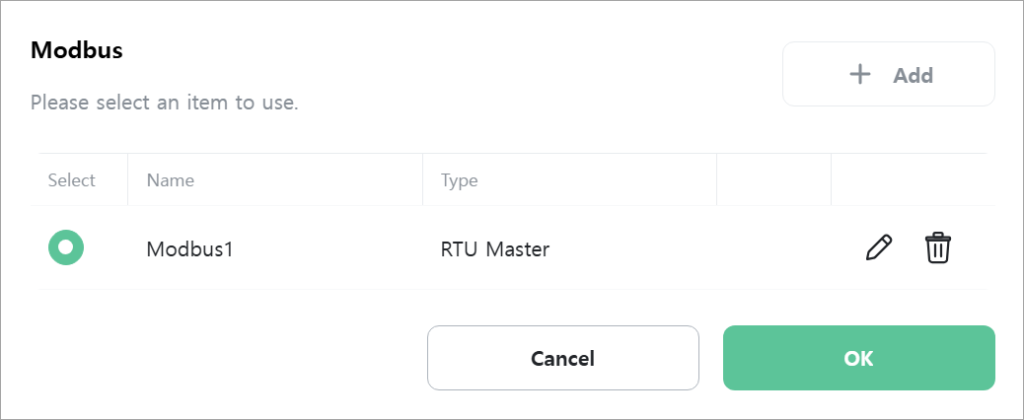
RTU/TCP Master
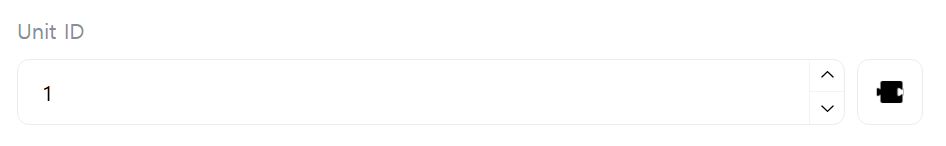
[Unit ID]
Enter the Unit ID of the Slave to communicate with.
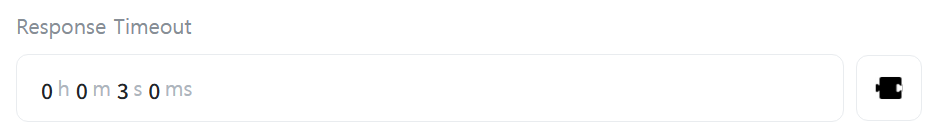
[Response Timeout]
Enter the response timeout duration for the Slave’s response to requests. If this time is exceeded, the connection to the Slave is considered lost.
[Function Code]
Enter the Function Code for the request.
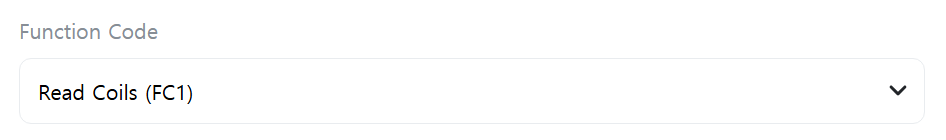
- Read Coils (FC1): Read multiple digital output states (coils)
- Read Discrete Inputs (FC2): Read multiple digital input states
- Read Holding Registers (FC3): Read multiple analog outputs (Holding Registers)
- Read Input Registers (FC4): Read multiple analog inputs (Input Registers)
- Write Single Coil (FC5): Write single digital output (coil) state
- Write Single Register (FC6): Write single register value
- Write Multiple Coils (FC15): Write multiple digital output states
- Write Multiple Registers (FC16): Write multiple registers
- Read/Write Multiple Registers (FC23): Read and write multiple registers
[Read Offset]
Enter the offset (address) of the Slave’s memory area to read data from. Only displayed when [Function Code] is “FC1”, “FC2”, “FC3”, “FC4”, or “FC23”.

[Read Length]
Enter the size of data to read from the Slave’s memory area. Only displayed when [Function Code] is “FC1”, “FC2”, “FC3”, “FC4”, or “FC23”.
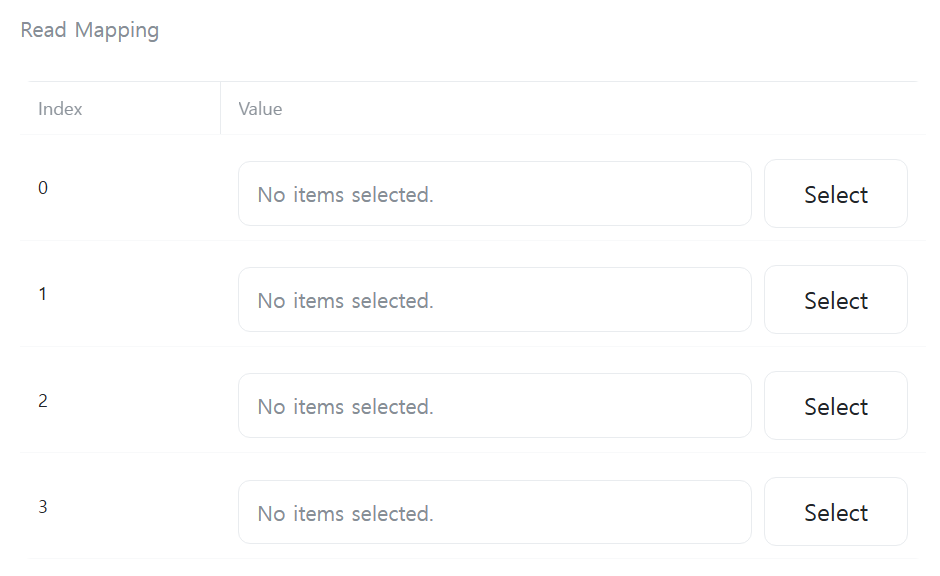
[Read Mapping]
Select variables to store the data read from the Slave. The number of table rows is determined by the value of [Read Length].
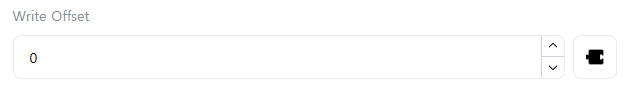
[Write Offset]
Enter the offset (address) of the Slave’s memory area to write data to. Only displayed when [Function Code] is “FC5”, “FC6”, “FC15”, “FC16”, or “FC23”.
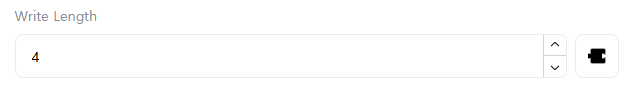
[Write Length]
Enter the size of data to write to the Slave’s memory area. Only displayed when [Function Code] is “FC5”, “FC6”, “FC15”, “FC16”, or “FC23”.
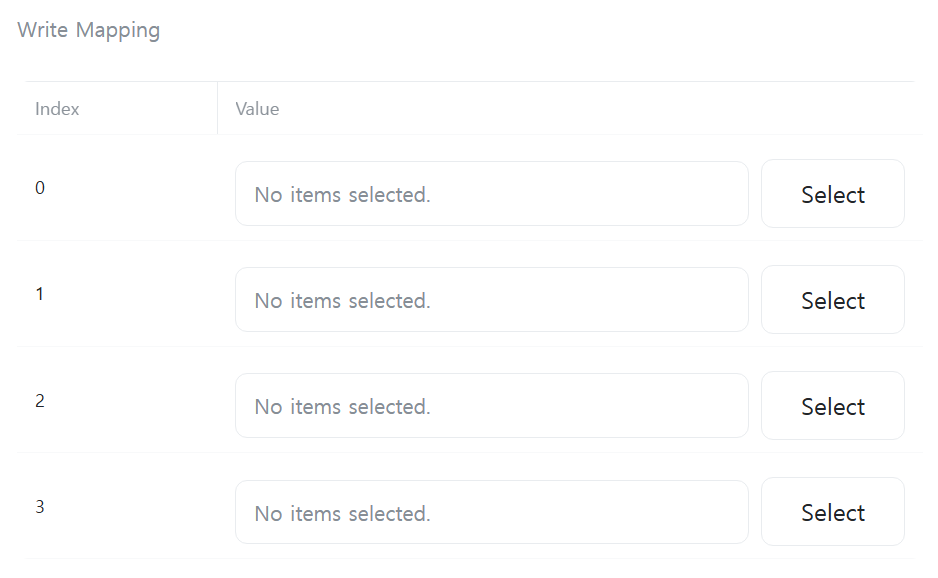
[Write Mapping]
Select variables that contain the data to write to the Slave. The number of table rows is determined by the value of [Write Length].
RTU/TCP Slave
Slave has no separate configuration items and processes Master requests each time the action is executed.
