PID Control
An action that calculates PID feedback control.
PID Control is a feedback control mechanism widely used in process control systems. PID stands for Proportional, Integral, and Derivative, which combine these three elements to minimize system error and maintain the desired target value.
[PID Control]
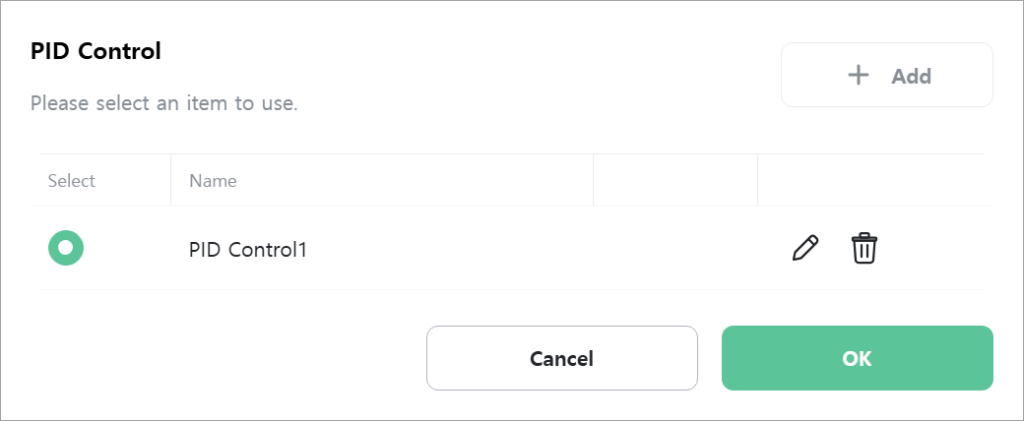
Select the PID control to use.

[Command]
Select the command to execute.

- Compute: Executes PID calculation. This command must be repeated at regular intervals.
- Stop: Stops PID calculation.
[Proportional Gain (Kp)]
Enter the proportional gain (Kp).

[Integral Gain (Ki)]
Enter the integral gain (Ki).

[Derivative Gain (Kd)]
Enter the derivative gain (Kd).

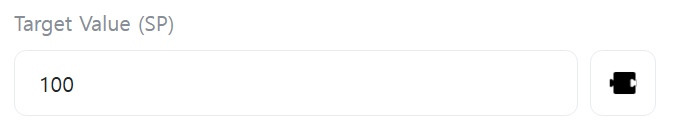
[Target Value (SP)]
Enter the target value (SP, Set Point). This represents the target value that the system should reach. (e.g., set temperature in a temperature control system)
[Input Value (PV)]
Select a variable to read the input value (PV, Process Variable). This represents the actual measured value from the system. (e.g., measured temperature in a temperature control system)
[Output Value (CV)]
Select a variable to store the output value (CV, Control Variable). This is the value output through PID calculation, representing the value that the system must adjust to reach the target value. (e.g., boiler valve opening angle in a temperature control system)

