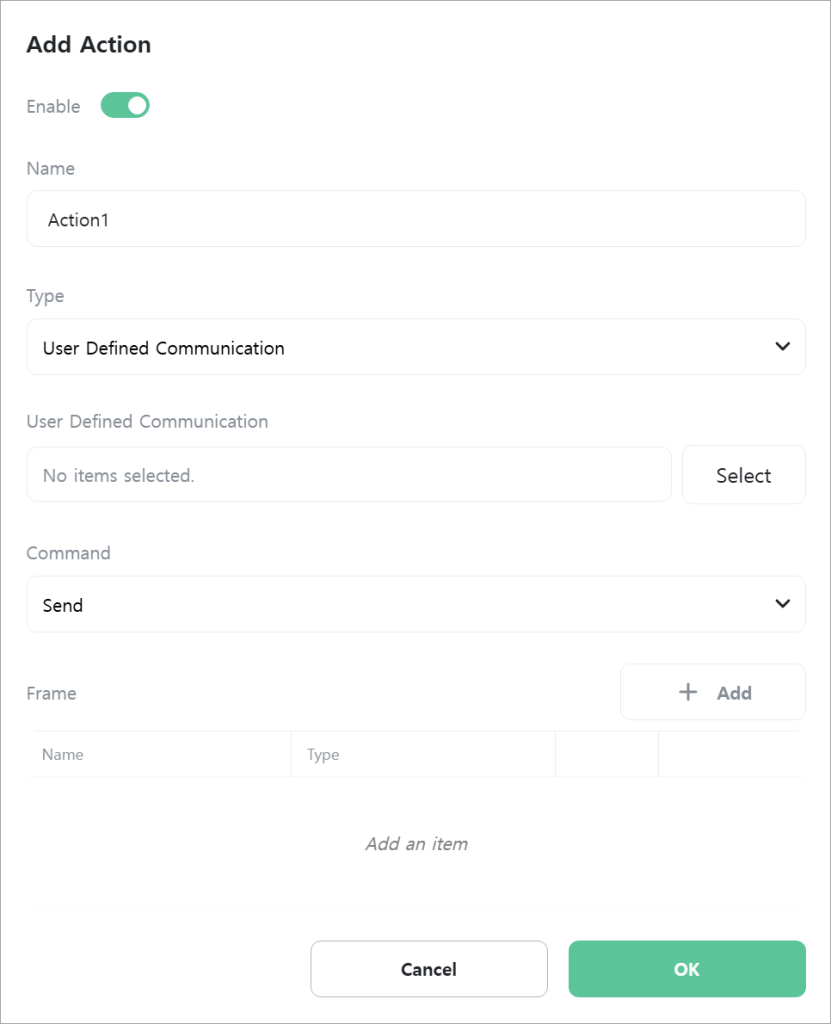
User Defined Communication
An action that allows users to define and use their own communication protocols. Communication is possible using serial communication, TCP, UDP, WebSocket, shared memory, and Bluetooth.
[User Defined Communication]
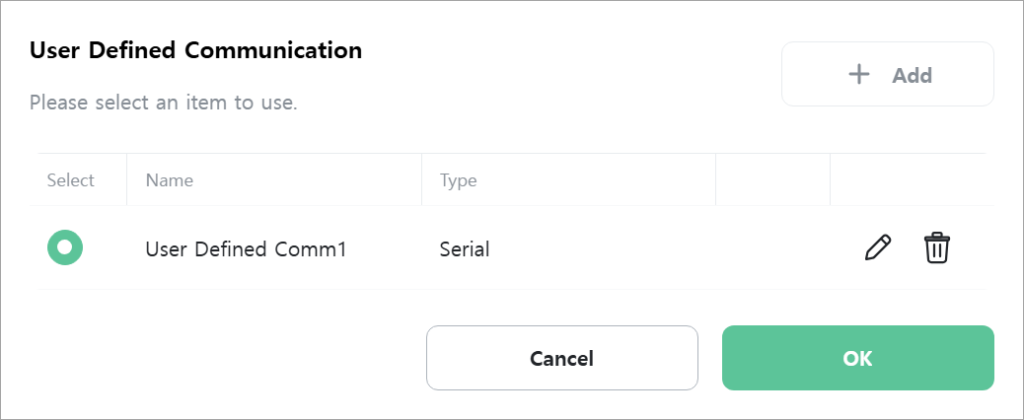
Select the user defined communication to use.

[Command]
Select the command to execute.

- Send: Transmits the configured data frame.
- Receive: Receives data.
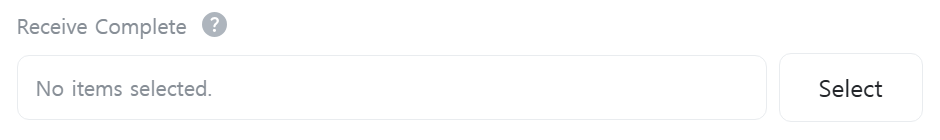
[Receive Complete]
Select a variable to store reception completion status. When new data is received, this variable becomes true, otherwise it becomes false. Only displayed when [Command] is “Receive”.
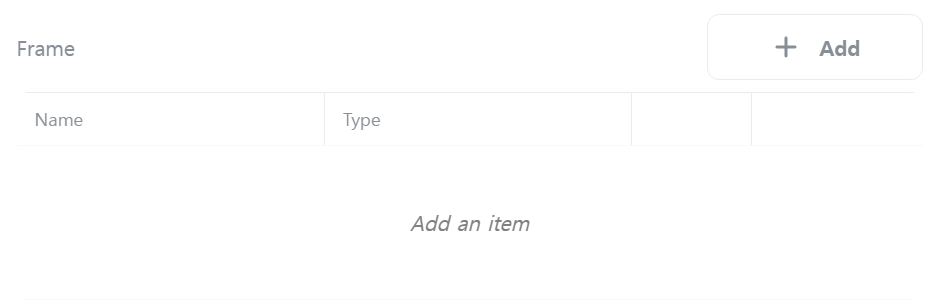
[Frame]
Configure the data frame to send or receive. The frame serves the following roles:
- When sending data
- Composes the data to be sent.
- Can include constants, variables, and integrity check data.
- If variables are included, the variable values at the time of sending are used.
- If integrity check data is included, the integrity of the sending data is checked and the calculation result is included in the frame.
- When receiving data
- Compares received data with frame data to check for matches.
- Can include constants, variables, and integrity check data.
- If variables are included, parses the received data and stores the values in variables.
- If integrity check data is included, performs integrity checks on the received data to verify that the results match.
> [Name]
Enter the name of the data. Any name can be used.
> [Type]
Select the type of data.

- Digital: A digital type constant that is true or false.
- Number: A numeric type constant. You can specify numeric formats such as byte size, integer/floating point.
- Text: A text type constant.
- Byte Array: A byte array type constant.
- Variable: Only [Digital], [Numeric], [String], and [Byte Array] type variables can be selected.
- Integrity Check: Checks data for errors and verifies integrity. Provides various calculation methods.
> [Value]
Enter a constant value. Only displayed when [Type] is “Digital”, “Number”, “Text”, or “Byte Array”.
> [Number Format]
Select the format of the number. Only displayed when [Type] is “Number”.

> [Unknown Byte Size]
Check this if the byte size of the data to receive is unknown. Only displayed when [Command] is “Receive” and [Type] is “Variable”. Only one variable with unknown byte size can exist in a frame.

> [Byte Size]
Enter the byte size of the data to receive. Parses and stores in the variable by this size. Only displayed when [Command] is “Receive” and [Type] is “Variable”.

> [Byte Reverse]
Reverses the byte order of data to be sent or received. Used when the communication partner has a different byte order (endian) handling method. Only displayed when the constant or variable type is “Number”, “Text”, or “Byte Array”.

> [Check Method]
Select the integrity check method for frame data. Checks integrity from [Start Data] to [End Data]. Only displayed when [Type] is “Integrity Check”.

- BYTE SUM: Calculates the sum by adding all bytes of data.
- WORD SUM: Calculates the sum by adding words (16-bit units) of data.
- BYTE XOR: Accumulates all bytes of data using XOR operation.
- 7BIT SUM: Removes the upper 1 bit from each data byte and calculates the sum by adding only the remaining 7 bits.
- 7BIT XOR: Removes the upper 1 bit from each data byte and accumulates only the remaining 7 bits using XOR operation.
- 7BIT SUM (≥ 0x20): Sums using 7 bits only for data bytes with values of 0x20 (space) or higher.
- BYTE SUM (2’s Complement): Adds all bytes and converts the sum to two’s complement to calculate the check value.
- BYTE SUM (1’s Complement): Adds all bytes and converts the sum to one’s complement (bit inversion) to calculate the check value.
- CRC16 STANDARD: Calculates 16-bit cyclic redundancy check (CRC) based on standard polynomial.
- CRC16 CCITT: Calculates 16-bit CRC based on CCITT standard polynomial (0x1021).
- CRC16 MODBUS: Calculates 16-bit CRC based on polynomial (0x8005) used in Modbus protocol.
> [Start Data]
Select the start data for integrity check. Only displayed when [Type] is “Integrity Check”.
> [End Data]
Select the end data for integrity check. Only displayed when [Type] is “Integrity Check”.
> [Convert to ASCII]
Converts integrity calculation data to ASCII. For example, if the calculation result is hexadecimal 0x9C, it is changed to string “9C”. Only displayed when [Type] is “Integrity Check”.

